Bighead Carp
Hypophthalmichthys nobilis
Fast Facts
Origin
Large rivers and lakes in eastern China and far eastern Russia.
Diet
Zooplankton, detritus and small invertebrates.
Life Span
16+ years
Size
Maximum of more than 80 pounds and nearly 5 feet in length.
Historical Occurrence
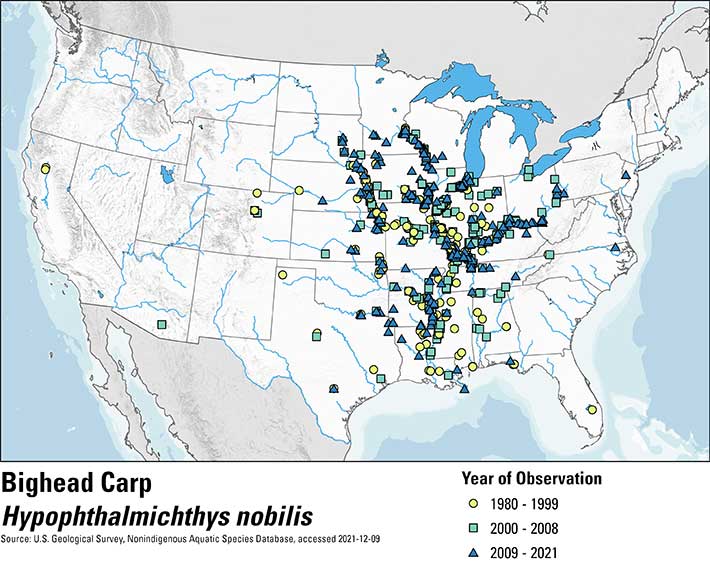 Historical occurrences of bighead carp in the United States. Data from the U.S. Geological Survey Nonindigenous Aquatic Species database, December 2021, represent reported observations of bighead carp, but populations may not be established in all mapped locations.
Historical occurrences of bighead carp in the United States. Data from the U.S. Geological Survey Nonindigenous Aquatic Species database, December 2021, represent reported observations of bighead carp, but populations may not be established in all mapped locations.
See current bighead carp occurrence data on the U.S. Geological Survey NAS database »

Background
Bighead Carp were imported from eastern China to Arkansas in the 1970s to improve water quality in aquaculture ponds and sewage treatment lagoons. The fish have since spread through the Mississippi River basin. Bighead carp have been captured as far north as Lake Pepin in Minnesota. The species was listed as "injurious" under the Lacey Act in 2011.
Physical Description
A bighead carp is a deep-bodied fish with a large toothless mouth and very large head. Their eyes are located forward and low on the head, well below the midline of the body. Coloration is dark gray above and cream-colored below with dark gray to black irregular blotches on the back and sides. Gill rakers are long, comb-like and close-set allowing the carp to strain plankton from the water for food. They have also been known to hybridiz, or cross-breed, with silver carp and produce viable, reproductive offspring.
Preferred Habitat
Spawning occurs in moderate to large rivers during the spring when water levels have risen due to spring flows. They can survive in cold water and begin to feed at water temperatures above 35° Fahrenheit, preferring temperatures of 39 to 78° Fahrenheit. Bighead carp can adapt to a broad range of temperate freshwater environments.
Diet
Bighead carp are voracious eaters and consume a wide range of zooplankton, detritus and small invertebrates, outcompeting native species for food. The bighead carp lacks a true stomach which requires it to feed almost continuously.
Size
Bighead carp mature in 2 to 3 years, commonly weighing up to 40 pounds, but under the right conditions they can grow to more than 80 pounds (rare).
